For twenty years, researchers labored to resolve a thriller in West Coast streams. Why, when it rained, had been giant numbers of spawning coho salmon dying? As a part of an effort to search out out, scientists positioned fish in water that contained particles of latest and outdated tires. The salmon died, and the researchers then started testing the a whole bunch of chemical substances that had leached into the water.
A 2020 paper revealed the reason for mortality: a chemical known as 6PPD that’s added to tires to forestall their cracking and degradation. When 6PPD, which happens in tire mud, is uncovered to ground-level ozone, it’s remodeled into a number of different chemical substances, together with 6PPD-quinone, or 6PPD-q. The compound is acutely poisonous to 4 of 11 examined fish species, together with coho salmon.
Thriller solved, however not the issue, for the chemical continues for use by all main tire producers and is discovered on roads and in waterways around the globe. Although nobody has studied the affect of 6PPD-q on human well being, it’s additionally been detected within the urine of youngsters, adults, and pregnant ladies in South China. The pathways and significance of that contamination are, up to now, unknown.
Seventy-eight p.c of ocean microplastics are artificial tire rubber, in accordance with one estimate.
Nonetheless, there at the moment are requires regulatory motion. Final month, the authorized nonprofit Earthjustice, on behalf of the fishing trade, filed a discover of intent to sue tire producers for violating the Endangered Species Act through the use of 6PPD. And a coalition of Indian tribes not too long ago known as on the EPA to ban use of the chemical. “Now we have witnessed firsthand the devastation to the salmon species we’ve got all the time relied upon to nourish our folks,” the Puyallup Tribal Council mentioned in a press release. “Now we have watched because the species have declined to the purpose of just about sure extinction if nothing is finished to guard them.”
The painstaking parsing of 6PPD and 6PPD-q was only the start of a worldwide marketing campaign to know the poisonous cocktail of natural chemical substances, tiny particles, and heavy metals hiding in tires and, to a lesser extent, brakes. Whereas the acute toxicity of 6PPD-q and its supply have sturdy scientific consensus, tire rubber incorporates greater than 400 chemical substances and compounds, a lot of them carcinogenic, and analysis is barely starting to point out how widespread the issues from tire mud could also be.

Researchers weigh a salmon that died after 4 hours in a tank crammed with highway runoff.
Ted S. Warren / AP Photograph
Whereas the rubber rings beneath your automobile could seem benign — one promoting marketing campaign used to characteristic infants cradled in tires — they’re, consultants say, a big supply of air, soil, and water air pollution that will have an effect on people in addition to fish, wildlife, and different organisms. That’s an issue as a result of some 2 billion tires globally are bought annually — sufficient to achieve the moon if stacked on their sides — with the market anticipated to achieve 3.4 billion a yr by 2030.
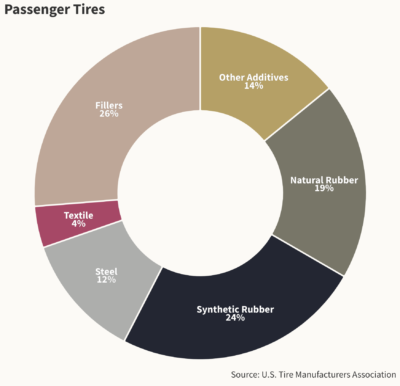
Tires are produced from about 20 p.c pure rubber and 24 p.c artificial rubber, which requires 5 gallons of petroleum per tire. Tons of of different elements, together with metal, fillers, and heavy metals — together with copper, cadmium, lead, and zinc — make up the remaining, a lot of them added to reinforce efficiency, enhance sturdiness, and scale back the potential for fires.
Each pure and artificial rubber break down within the atmosphere, however artificial fragments final lots longer. Seventy-eight p.c of ocean microplastics are artificial tire rubber, in accordance with a report by the Pew Charitable Belief. These fragments are ingested by marine animals — particles have been present in gills and stomachs — and may trigger a spread of results, from neurotoxicity to development retardation and behavioral abnormalities.
Tire emissions from electrical automobiles are 20 p.c greater than these from fossil-fuel automobiles.
“We discovered extraordinarily excessive ranges of microplastics in our stormwater,” mentioned Rebecca Sutton, an environmental scientist with the San Francisco Estuary Institute who studied runoff. “Our estimated annual discharge of microplastics into San Francisco Bay from stormwater was 7 trillion particles, and half of that was suspected tire particles.”
Tire put on particles, or TWP as they’re typically identified, are emitted regularly as automobiles journey. They vary in dimension from seen items of rubber or plastic to microparticles, and so they comprise one of many merchandise’ most vital environmental impacts, in accordance with the British agency Emissions Analytics, which has spent three years learning tire emissions. The corporate discovered {that a} automobile’s 4 tires collectively emit 1 trillion ultrafine particles — of lower than 100 nanometers — per kilometer pushed. These particles, a rising variety of consultants say, pose a novel well being threat: They’re so small they’ll go by lung tissue into the bloodstream and cross the blood-brain barrier or be breathed in and journey on to the mind, inflicting a spread of issues.
In line with a current report issued by researchers at Imperial School London, “There may be rising proof that tyre put on particles and different particulate matter could contribute to a spread of destructive well being impacts together with coronary heart, lung, developmental, reproductive, and most cancers outcomes.”
Yale Atmosphere 360
The report says that tires generate 6 million tons of particles a yr, globally, of which 200,000 tons find yourself in oceans. In line with Emissions Analytics, automobiles within the U.S. emit, on common, 5 kilos of tire particles a yr, whereas automobiles in Europe, the place fewer miles are pushed, shed 2.5 kilos per yr. Furthermore, tire emissions from electrical automobiles are 20 p.c greater than these from fossil-fuel automobiles. EVs weigh extra and have higher torque, which wears out tires quicker.
Not like tailpipe exhaust, which has lengthy been studied and controlled, emissions from tires and brakes — which emit vital quantities of metallic particles along with natural chemical substances — are far more durable to measure and management and have subsequently escaped regulation. It’s solely within the final a number of years, with the event of latest applied sciences able to measuring tire emissions and the alarming discovery of 6PPD-q, that the topic is receiving a lot wanted scrutiny.
Latest research present that the mass of PM 2.5 and PM 10 emissions — that are, together with ozone and ultrafine particles, the world’s major air pollution — from tires and brakes far exceeds the mass of emissions from tailpipes, not less than in locations which have considerably diminished these emissions.
Tires launch 100 instances the quantity of unstable natural compounds as a contemporary tailpipe, says an analyst.
The issue isn’t simply rubber in its artificial and pure kind. Authorities and educational researchers are investigating the transformations produced by tires’ many different elements, which might — like 6PPD — kind substances extra poisonous than their dad or mum chemical substances as they break down with publicity to daylight and rain.
“You’ve bought a chemical cocktail in these tires that nobody actually understands and is saved extremely confidential by the tire producers,” mentioned Nick Molden, the CEO of Emissions Analytics. “We wrestle to think about one other shopper product that’s so prevalent on this planet, and utilized by nearly everybody, the place there may be so little identified of what’s in them.”
“Now we have identified that tires contribute considerably to environmental air pollution, however solely not too long ago have we begun to uncover the extent of that,” mentioned Cassandra Johannessen, a researcher at Montreal’s Concordia College who’s quantifying ranges of tire chemical substances in city watersheds and learning how they remodel within the atmosphere. The invention of 6PPD-q has stunned a variety of researchers, she mentioned, as a result of they’ve discovered that “it’s some of the poisonous substances identified, and it appears to be in all places on this planet.”
Regulators are enjoying catch up. In Europe, a typical to be applied in 2025, referred to as Euro 7, will regulate not solely tailpipe emissions but in addition emissions from tires and brakes. The California Environmental Safety Company has handed a rule requiring tire makers to declare a substitute for 6PPD by 2024.

A employee takes aside a tire at a recycling store in Mit al-Harun, Egypt.
Khaled Desouki / AFP
Tire firms are conducting their very own research of 6PPD, which they’ve lengthy thought of important for tire security, and looking for options. In response to new rules and the rising analysis on tire emissions, 10 of the world’s giant tire producers have fashioned the Tire Business Challenge to “develop a holistic strategy to raised perceive and promote motion on the mitigation” of tire air pollution, in accordance with a press release by the venture. The group has dedicated to seek for methods to revamp tires to scale back or eradicate emissions.
One important space of analysis is how lengthy tire waste, and its breakdown merchandise, persist within the atmosphere. “A five-micron piece of rubber shears off the tire and settles on the soil and sits there some time,” mentioned Molden. “What, over time, is the discharge of these chemical substances, how rapidly do they make their means into the water, and are they diluted? On the system degree, how massive of an issue is that this? It’s the single largest information hole.”
One other space of analysis facilities on the impacts of fragrant hydrocarbons — together with benzene and naphthalene — off-gassed by artificial rubber or emitted when discarded tires are burned in incinerators for power restoration. Even at low concentrations, these compounds are poisonous to people. In addition they react with daylight to kind ozone, or ground-level smog, which causes respiratory hurt. “Now we have proven that the quantity of off-gassing unstable natural compounds is 100 instances higher than that popping out of a contemporary tailpipe,” mentioned Molden. “That is from the tire simply sitting there.”
Scientists discovered that rain gardens might stop greater than 90 p.c of a harmful tire pollutant from getting into streams.
When tires attain their finish of life, they’re both despatched to landfills, incinerated, burned in an energy-intensive course of known as pyrolysis, or shredded and repurposed to be used in synthetic turf or in playgrounds or for different surfaces. However as concern about tire pollution grows, so do issues about these recycled merchandise and the hydrocarbons they could off-gas. There may be ongoing debate over whether or not crumb rubber, produced from tire scraps, poses a well being risk when used to fill gaps in synthetic turf. Primarily based on a number of peer-reviewed research, the European Union is instituting stricter limits on the usage of this materials. Different research, nonetheless, have proven no well being affect.
Moreover California’s requirement to check options to 6PPD, there are a variety of efforts worldwide to revamp tires to counter the issues they pose. Greater than a decade in the past, tire makers hoped that dandelions, which produce a type of rubber, and soy oil might present a gradual and sustainable provide of rubber. However tires produced from these options didn’t stay as much as expectations: they nonetheless required components. The Continental Tire Firm, based mostly in Hanover, Germany, markets a bicycle tire product of dandelion roots. Examined by Emission Analytics, it emitted 25 p.c fewer carcinogenic aromatics than conventionally made bike tires, however the plant-powered tire nonetheless contained elements of concern.

Rubber produced from dandelions.
Continental
Different firms are trying to find methods to handle the issue of tire emissions. The Tyre Collective, a clean-tech startup based mostly within the U.Ok., has developed an electrostatic plate that affixes to every of a automobile’s tires: The plates take away as much as 60 p.c of particles emitted by each tires and brakes, storing them in a cartridge hooked up to the machine. The particles might be reused in quite a few different functions, together with in new tires.
In San Francisco, scientists learning the pollution in storm runoff discovered a possible answer: Rain gardens, put in in yards to seize stormwater, had been additionally trapping 96 p.c of road litter and 100% of black rubbery fragments. In Vancouver, B.C. researchers discovered that rain gardens might stop greater than 90 p.c of 6PPD-q from working off roads and getting into salmon-bearing streams.
Tire waste particles, says Molden, of Emissions Analytics, are lastly getting the eye they deserve, thanks partly to California’s rule requiring a seek for options to 6PPD. The laws “is groundbreaking,” he says, “as a result of it places the chemical composition [of tires] on the regulatory agenda.” For the primary time, he provides, “Tire producers are being uncovered to the identical regulatory scrutiny that automobile producers have been for 50 years.”
