Sequoia Nationwide Park’s well-known groves of stout, 300-foot-tall timber sit excessive on the western facet of the Sierra Nevada, above California’s San Joaquin Valley. They’re threatened as by no means earlier than: Wildfires have burned a lot of the forest, and now, for the primary time, bugs are killing sequoias.
There may be additionally a stealthier risk to those majestic timber and the forest ecosystem of which they’re an element. Ozone ranges at Sequoia and the adjoining nationwide park, King’s Canyon, are among the many highest in the USA, due to smog that blows in from the city areas and farming and industrial exercise within the San Joaquin Valley under. Smog ranges listed here are typically as excessive, or increased, than they’re in Los Angeles.
It has lengthy been identified that floor stage, or tropospheric, ozone damages timber and different vegetation by affecting a number of organic processes on the mobile stage. Research have proven that top ozone ranges negatively affect plant progress, vitality, photosynthesis, water steadiness, the flowering course of, and the skills of vegetation to defend themselves.
Extra lately, researchers have turned their consideration to how the detrimental results of ozone on flora can ripple by means of total ecosystems and affect biodiversity, harming bugs, wildlife, and even soil.
Research present that these knock-on results can embrace making vegetation much less nutritious; diminishing the scent trails pollinators comply with to seek out their goal; altering the timing of leaf fall, affecting the forest flooring and the microbial communities that inhabit it; impacting the basis programs of vegetation and timber and the microbes, fungi, and different organisms that stay there; and even decreasing harvests of staple meals crops equivalent to corn and wheat. And scientists predict that these unfavorable results will develop worse because the planet warms since ground-level ozone will increase as temperatures rise.
Hotter climate will increase ground-level ozone, an issue that’s predicted to worsen.
The impacts from ozone within the Sierras and elsewhere are removed from absolutely understood, as a result of the results are tough to check, and analysis hasn’t been nicely funded. It may be tough to tease out the results of ozone from different stressors equivalent to drought and hotter temperatures, and lots of the modifications from ozone will not be detectable for years or a long time.
However analysis to this point exhibits that elevated ozone ranges are already taking a toll on biodiversity in myriad methods
“Ozone is essentially the most damaging pollutant on the planet,” mentioned Evgenios Agathokleous, a professor of environmental sources on the Institute of Ecology at Nanjing College of Data Science & Expertise in China and one of many high researchers within the subject. “It induces essentially the most widespread injury to vegetation, and it’s a really severe risk to biodiversity.” In some components of Asia, he mentioned, ozone ranges are 10 instances the crucial thresholds.
Ozone — an invisible, odorless fuel within the higher ambiance — is important for all times as a result of it shields the earth from the solar’s dangerous ultraviolet rays. The 1987 Montreal Protocol phasing out industrial chemical compounds that had been destroying the ozone layer is taken into account one of the vital profitable worldwide environmental actions ever taken. At floor stage, although, ozone is poisonous to life. “Good up excessive, dangerous close by” is the phrase some scientists use. It’s also a greenhouse fuel — the third worst after carbon dioxide and methane.
Floor-level ozone is created principally by people, shaped by pollution — equivalent to nitrous oxide, methane, and risky natural compounds — which might be emitted by vehicles, vans, refineries, energy vegetation, and oil and fuel improvement. It’s chemically just like chlorine, however not as poisonous.

Large sequoias in Sequoia Nationwide Park, California.
Marji Lang/LightRocket through Getty Photos
When these airborne pollution meet daylight and heat temperatures, they undergo a chemical response and turn into ozone. Within the U.S., ozone has decreased considerably in latest a long time due to laws governing the emission of nitrous oxide and different precursor pollution. But there are locations the place ozone stays at excessive ranges, together with a lot of the West. Along with Sequoia Nationwide Park, ozone ranges stay very excessive in different parks, together with Joshua Tree and Rocky Mountain nationwide parks. Denver, Salt Lake Metropolis, and Albuquerque, amongst different city areas within the West, typically attain health-threatening ranges of ozone.
Research present ozone ranges are growing steadily throughout the complete Asia-Pacific area, Africa, and Europe. The supply of most of it’s China, India, and southeast Asia. And ozone can journey huge distances — rising up from northern India to envelop the Himalayas or crossing the Pacific from Asia to turn into a consider ozone ranges on the West Coast, together with the ozone affecting sequoias. Ozone has additionally been cited in injury to vegetation within the Arctic.
As well as, hotter climate will increase ground-level ozone, an issue that’s predicted to worsen. “In case you are beneath polluted situations because the local weather warms, you get extra ozone,” mentioned Daniel Jacobs, a professor of atmospheric chemistry at Harvard College who research ozone, air air pollution, and methane. “Three causes: there’s extra stagnation and accumulation of polluted air, the reactions that trigger ozone occur sooner because it will get hotter, and nitrous oxide (a precursor) has an extended lifetime in hotter temperatures.” Worsening air air pollution from local weather change is usually known as the “local weather penalty.”
In the meantime, methane ranges within the ambiance have been growing quickly since 2006 and final yr hit document highs. Along with being a potent greenhouse fuel, methane can also be an ozone precursor.
Ozone does extra injury to vegetation than all different air pollution mixed, the USDA says.
It’s nicely established that continual publicity to excessive ozone ranges is a severe risk to human well being, exacerbating coronary heart and lung issues equivalent to bronchial asthma and emphysema, and inflicting decreased beginning weights. One research discovered that greater than 1 million untimely deaths are triggered globally annually by excessive ranges of ozone.
Analysis additionally exhibits that crops and forests are broken or killed by ozone, both straight or not directly, as ozone makes them extra vulnerable to bugs, illness, and drought. Ozone does extra injury to vegetation than all different air pollution mixed, based on the U.S. Division of Agriculture. The fuel is predicted to trigger a considerable decline in world meals manufacturing. One latest research predicted that by 2050 wheat manufacturing would decline by 13 %, soybeans by 28 %, and corn by 43 % due to rising temperatures and ozone.
Whereas it’s clear that ozone can take a toll on all residing organisms, analysis has not, till lately, checked out its results on biodiversity. Scientists consider, nevertheless, that the impacts are substantial. This month the Worldwide Union of Forest Analysis Organizations, a world community of scientists, is holding a convention on Air Air pollution Threats to Plant Ecosystems. Ozone is on the high of the record.
In a paper printed final yr, 20 researchers in Europe and Asia, together with Agathakleous, modeled what may occur to ecosystems in coming a long time on account of ozone air pollution. They concluded that ozone will have an effect on “the composition and variety of plant communities by affecting key physiological traits” and may trigger a cascade of modifications that diminish biodiversity. Of their paper, the researchers urged officers to take ozone under consideration in efforts to guard and restore biodiversity and mentioned its results must be included in assessments of atmospheric air pollution and local weather change.
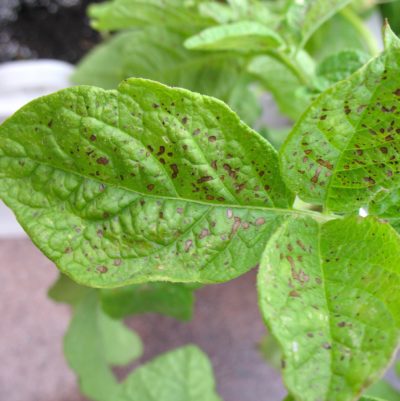

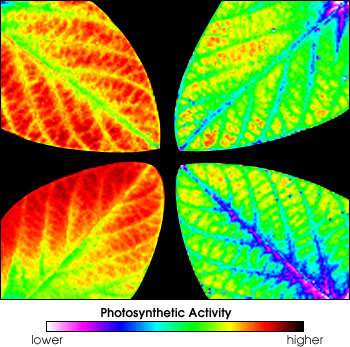
Left: Brown patches on potato leaves present proof of ozone injury. Proper: Fluorescence imaging reveals the distinction in photosynthetic exercise between soybean leaves grown in wholesome situations (left) and people grown in chambers with elevated ozone ranges (proper).
Danica Lombardozzi / NCAR;
Analysis is exhibiting that ozone impacts vegetation in all kinds of how.
“It paralyzes the vegetation’ stomata,” mentioned Howard Neufeld, a plant ecologist at Appalachian State College, “and they also launch extra water than they soak up.” Stomata are the microscopic openings on the floor of leaves the place timber trade gasses with the ambiance. Ozone damages them and interferes with a wide range of processes, together with photosynthesis.
Ozone additionally damages leaves and accelerates their getting old. “As leaves are injured, photosynthesis goes down; a plant makes much less sugars, and it has fewer sources,” says Neufeld. “It additionally impacts the motion of sugars to roots, which reduces root progress, making them extra vulnerable to drought and nutrient deficiencies and illness.”
Ozone injury also can alter the timing of leaf fall and shrink leaf dimension, decreasing the quantity of litter and affecting the microbial communities that thrive in decomposing leaves. Microbes within the litter and soil are crucial to taking on vitamins, serving to timber resist illness and use water effectively.
Ozone’s impacts on soil additionally have an effect on the rhizosphere — the basis system and its related microbes, fungi, and different organisms. “When the vegetation reply to ozone, they eat vitality,” mentioned Agathokleous. “After they use a lot vitality, there’s much less to offer to organisms within the soil and the chemical composition may be affected.” Much less nutritious leaves also can have an effect on the life cycle of animals that feed on them.
Ozone is just not an equal alternative pollutant — some vegetation are extremely vulnerable to the poisonous fuel and others much less so. Within the U.S. for instance, black cherry, quaking aspen, and white pine are among the many species most affected. These disparate impacts are behind one of many main impacts of ozone on ecosystems — it modifications the composition of the plant neighborhood and reduces species richness. Some species of vegetation might decline or disappear, whereas others thrive as a result of they not have the identical competitors. Insect and wildlife species that rely upon these vegetation are additionally affected

Smog shrouds the Kathmandu Valley in Nepal, within the foothills of the Himalayas.
Frank Bienewald/LightRocket through Getty Photos
Research in California’s San Bernadino Mountains have proven that ozone elevated forest susceptibility to wildfire as a result of ozone-sensitive, fire-resistant species of pine had been changed by species that had been extra more likely to burn.
Chemical elements of an ecosystem additionally undergo myriad modifications on account of ozone. The fuel reduces the quantity of nitrogen within the leaves of vegetation, for instance, a key nutrient that drives insect dynamics.
Ozone alters the biogenic risky natural compounds which might be emitted by vegetation, all the pieces from isoprene to terpenes. These chemical compounds are how vegetation sign to different vegetation, bugs, and animals. Relations between bugs and the chemical compounds these vegetation emit are, the paper says, “extremely advanced” and are crucial to ecosystem capabilities.
One paper, for instance, discovered that ozone diminished the floral scent that pulls pollinators. These messenger odors inform a bee or different pollinator a half-mile away how a lot pollen is accessible, the standard, and what species it’s. However increased ozone ranges degraded the scent, and pollinators had been much less profitable to find the goal plant. A latest paper discovered that ozone additionally diminished the olfactory talents of pollinators, decreasing their capability to detect pollen sources.
Consultants say different bugs, mammals, and birds are more likely to undergo deleterious impacts from ozone, simply as people do. Agathokleous mentioned that analysis is vital not solely to grasp the threats to current biodiversity however to information restoration efforts. However the invisible nature of the risk has been an obstacle to attracting the mandatory funding.
“Local weather change may be seen or felt, whether or not it’s elevated rain, drought, or warmth,” says Agathakleous. “Ozone air pollution is a hidden drawback. It can not generally be seen or felt. Individuals don’t take note of one thing they can’t see.”
Analysis for this text was supported by the Invoice Lane Heart for the American West at Stanford College.
